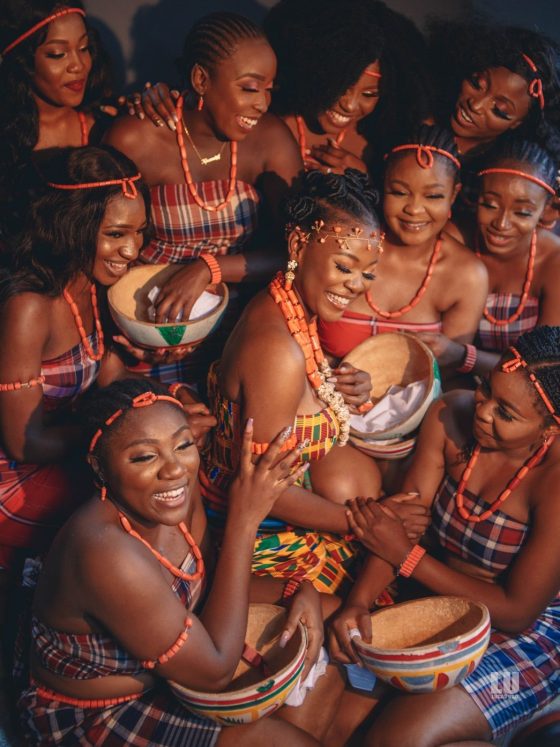
Have you noticed that some traditions quietly fade over time?
Folk songs once sung at harvests or weddings are performed less frequently; local folktales about heroes and spirits are told less often; and indigenous languages are disappearing as fewer people speak them.
As a result, the younger generation only knows a little of their cultural heritage. In this article, we examine how art, as social memory in a rapidly changing world, helps people preserve shared history even as life continues to change.
Read our detailed guide to learn how art as social memory in a rapid world keeps traditions, stories, and values alive across generations.
Understanding Art As Social Memory In A Rapid World
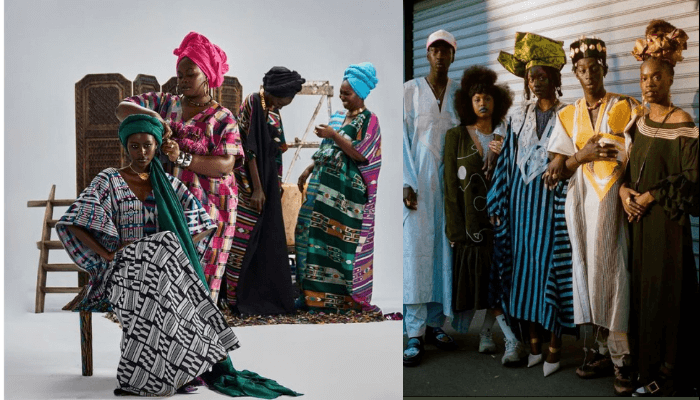
Social memory lives in the creative expressions people share. It exists in songs passed down through generations, symbols used in traditional clothing, stories told through film, and images captured in visual art.
These creative forms do more than entertain. They preserve experiences, values, and histories that may not exist in written records. Through art, communities document who they are, where they come from, and what they have lived through.
This is why art serves as social memory. It transmits cultural knowledge, enabling each generation to understand its identity and remain connected to its roots, even as society continues to evolve.
Why The Modern Rapid World Threatens Cultural Memory
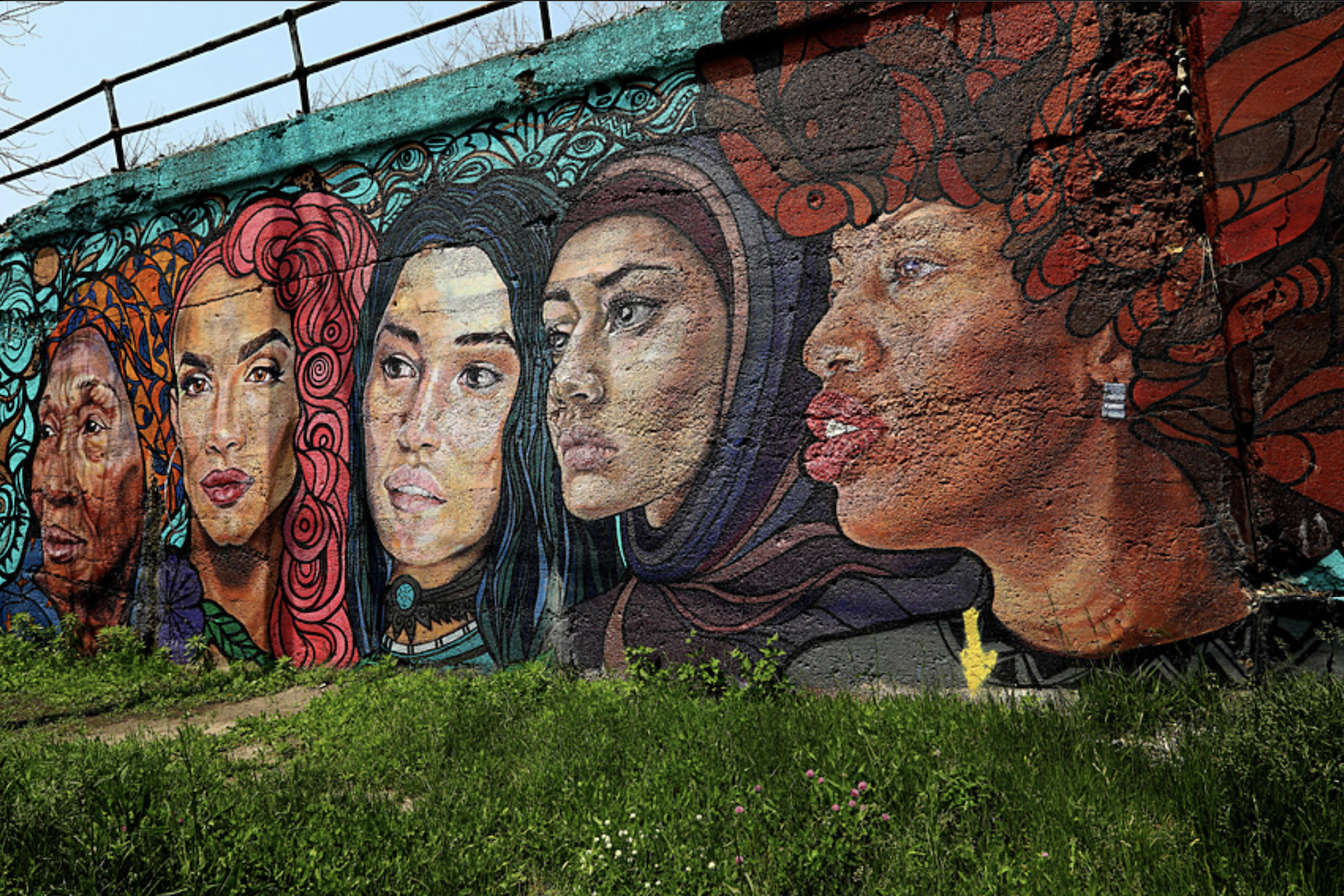

Currently, preserving cultural identity is a challenge for some communities. This disrupts the usual ways of passing knowledge, such as storytelling, crafts, and rituals. Some of the key challenges include:
1. Traditions Fading Over Time
Cultural rituals, ceremonies, and community practices are performed less frequently, weakening heritage preservation and reducing opportunities for younger generations to engage with shared history.
2. Language And Cultural Knowledge Loss
When native languages are spoken less, the critical cultural knowledge embedded in them, proverbs, oral history, and traditional expressions disappear, creating gaps in social memory.
3. Influence Of Global Trends On Local Identity
Dominant global media and lifestyle trends can overshadow local customs, traditional values, and community practices, putting cultural identity in rapid jeopardy.
4. Short Attention Spans And Fast-Moving Digital Culture
Social media and digital platforms prioritise quick, trending content over in-depth storytelling, reducing exposure to traditional narratives and practices that preserve social memory.
5. Generational Gaps In Heritage Transmission
Younger generations may grow up with only fragments of cultural history, leaving them disconnected from traditions, rituals, and symbols that once defined community identity.
Understanding these pressures helps explain why art, as social memory in a rapidly changing world, is essential for preserving cultural identity, heritage, and intergenerational knowledge.
How Art Preserves Social Memory In A Rapid World
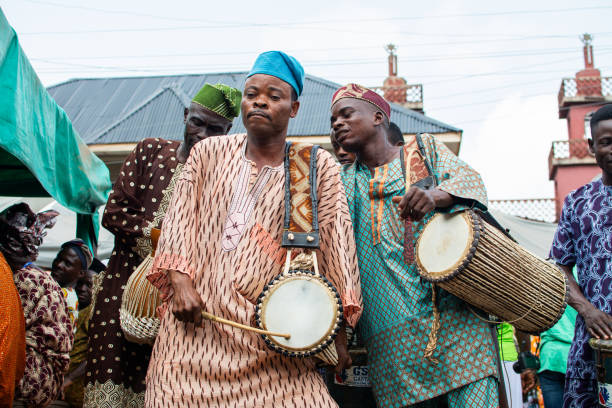

Even with cultural knowledge at risk, art serves as a bridge between generations. It carries stories, emotions, and symbols that help communities maintain their identity.
Here are key ways art preserves social memory:
1. Music Captures History And Identity
Songs and rhythms reflect social struggles, achievements, and daily life. Traditional music preserves language and rituals, while modern adaptations help younger generations connect with heritage.
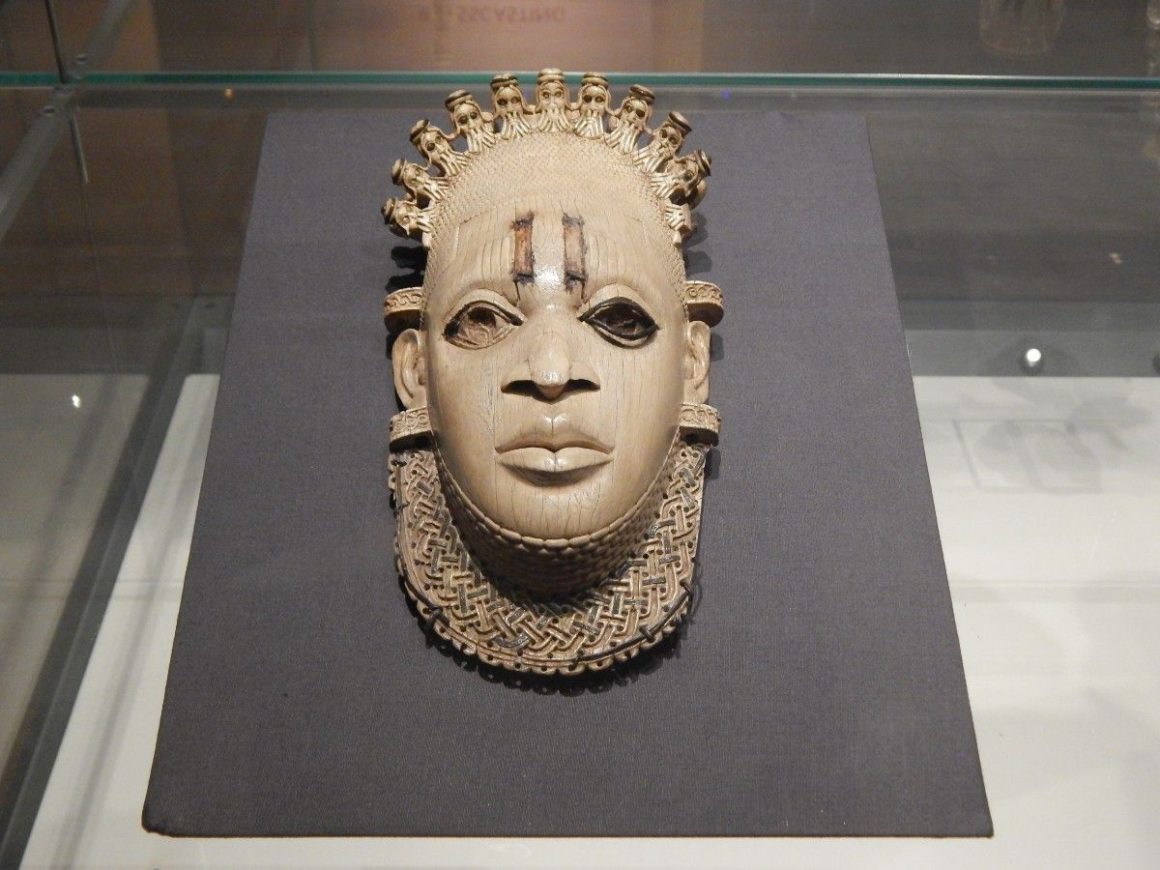
2. Visual Art Records Community Life
Visual art documents historical moments and cultural practices, preserving collective memory even in the absence of written records.
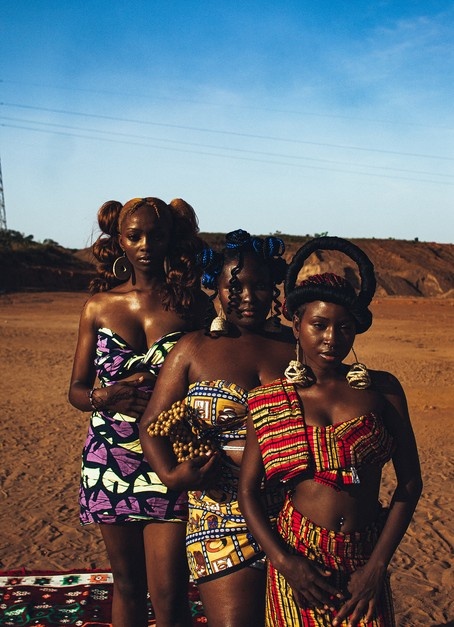
3. Fashion And Crafts Carry Heritage
Clothing, textiles, jewellery, and craft designs embed symbols and stories unique to a community, thereby sustaining their traditions in daily life.
4. Storytelling Passes Knowledge
Oral stories, folktales, plays, and written works preserve morals, traditions, and history. Modern formats like books, digital media, and film make cultural memory accessible to younger generations.
5. Film And Digital Media Make Memory Visible
Documentaries, feature films, and online storytelling capture history and rituals while providing communities with broader avenues to share and engage with heritage.
Together, these forms help communities retain cultural identity, connect generations, and keep traditions alive in a rapidly changing world.
The Role Of Artists As Memory Keepers
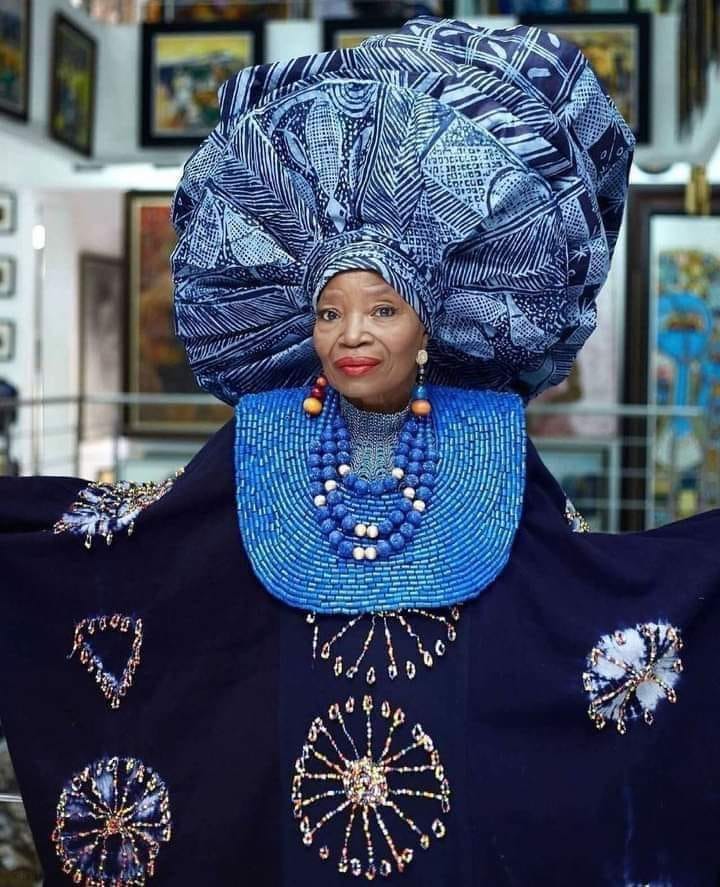

Artists are essential to preserving social memory in a rapidly changing world. They capture cultural traditions, historical events, and community stories that might otherwise be forgotten, using creative forms that people can experience and relate to.
Modern tools give artists new ways to preserve social memory. Digital projects, online storytelling, and contemporary reinterpretations of traditional crafts make heritage accessible to wider audiences.
Artists serve as cultural historians, bridging intergenerational knowledge gaps and sustaining traditions amid globalisation and rapid societal change.
Through their work, communities can retain shared history, values, and identity, demonstrating how art, as social memory in a rapid world, safeguards cultural heritage in a fast-moving era.
INTERESTING READS:
- When Creativity Resists Erasure: How Culture Lives On Through Art
- Opera Was Never White: Black Singers and the Truth About Classical Music
- Why Culture Is the Foundation of Style in African and Global Fashion
- How African Drums Shape Global Music: The Real Backbone of Modern Sound
Challenges Facing Art As Social Memory In A Rapid World

Preserving social memory through art isn’t without obstacles. Communities and artists face pressures that can weaken the impact of creative work.
Here are some challenges that art faces as a form of social memory in a rapidly changing world:
- Culture for Profit: Sometimes traditions or art are used to make money, and people forget the real meaning behind them.
- Losing Knowledge from Elders: Older people who know traditions may pass away without teaching the younger generation, resulting in the loss of some knowledge.
- Insufficient Support for Artists: Many artists lack the funds or tools to create projects that sustain cultural memory.
- Misrepresenting Traditions: Sometimes traditions are misunderstood or copied in the wrong way, which can change or confuse their original meaning.
- Fast-Changing Lifestyles: Cities, technology, and busy modern life make it harder for people to take part in traditional art and cultural activities.
These challenges point out why communities must actively support art as a tool for heritage preservation and cultural continuity.
Conclusion
With change happening faster than ever, art serves as a living memory. It transmits customs, narratives, and cultural identity among successive generations, safeguarding what could otherwise vanish.
Creative works preserve traditions, stories, and values, connecting generations and keeping shared history alive. Supporting artists and engaging with cultural heritage ensures that communities remember who they are.
Art, as a form of social memory, helps safeguard cultural identity and keep traditions alive, allowing societies to remain connected to their roots even as life changes.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What Is Art As Social Memory In A Rapid World?
It is the way creative works, such as music, art, storytelling, and performance, help communities preserve shared history and cultural identity in a rapidly changing world.
2. Why Is Art Important For Preserving Culture?
Art preserves traditions, values, and historical experiences, helping communities remember who they are.
3. Can Digital Tools Help Preserve Cultural Memory?
Yes. Digital art, online storytelling, and modern platforms make heritage accessible and engaging for younger generations.
3. How Does Globalisation Affect Culture?
Global trends can overshadow local customs and values, making it harder to maintain shared cultural knowledge.
4. How Do Young People Connect With Culture Through Art?
Art translates traditions and history into experiences that are engaging and easy to understand.